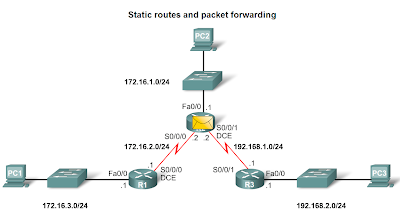
- Packet forwarding with static routes. (recall Zinin’s 3 routing principles)
- Router 1 Packet arrives on R1’s Fastethernet 0/0 interface R1 does not have a route to the destination network, 192.168.2.0/24 R1 uses the default static route.
- Packet forwarding with static routes. (recall Zinin’s 3 routing principles)
- Router 2
- The packet arrives on the Serial 0/0/0 interface on R2
- .R2 has a static route to 192.168.2.0/24 out Serial0/0/1.
- Packet forwarding with static routes. (recall Zinin’s 3 routing principles)
- Router 3
- The packet arrives on the Serial0/0/1 interface on R3.
- R3 has a connected route to 192.168.2.0/24 out Fastethernet 0/1
- Troubleshooting a Missing Route
- Tools that can be used to isolate routing problems include:
- Ping– tests end to end connectivity
- Traceroute– used to discover all of the hops (routers) along the path between 2 points
- Show IP route– used to display routing table & ascertain forwarding process
- Show ip interface brief- used to show status of router interfaces
- Show cdp neighbors detail– used to gather configuration information about directly connected neighbors
- Solving a Missing Route
- Finding a missing or mis-configured route requires methodically using the correct tools
-Start with PING. If ping fails then use traceroute to determine where packets are failing to arrive - Issue: show ip route to examine routing table.
-If there is a problem with a mis-configured static route remove the static route then reconfigure the new static route
- Solving a Missing Route
Summary
- Routers
- Operate at layer 3
- Functions include best path selection & forwarding packets
- Connecting Networks
- WANs Serial cables are connected to router serial ports. In the lab environment clock rates must be configured for DCE
- LANs Straight through cables or cross over cables are used to connect to fastethernet port. (The type of cable used depends on what devices are being connected)
- Cisco Discovery Protocol
- A layer 2 proprietary protocol Used to discover information about directly connected Cisco devices
- Static Routes
- This is a manually configured path that specifies how the router will get to a certain point using a certain path.
- Summary static routes
- This is several static routes that have been condensed into a single static route.
- Default route
- It is the route packets use if there is no other possible match for their destination in the routing table.
- Forwarding of packets when static route is used
- Zinin’s 3 routing principles describe how packets are forwarded
- Troubleshooting static routes may require some of the following commands:
- Ping
- Traceroute
- Show cdp neighbors detail
- Show IP route
- Show ip interface brief










No comments:
Post a Comment