Objectives
- Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1’s limitations.
- Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) configuration commands and evaluate RIPv2 classless routing updates.
- Analyze router output to see RIPv2 support for VLSM and CIDR
- Identify RIPv2 verification commands and common RIPv2 issues.
- Configure, verify, and troubleshoot RIPv2 in “handson” labs
Introduction
- RIPv1
- A classful distance vector routing protocol
- Does not support discontiguous subnets
- Does not support VLSM
- Does not send subnet mask in routing update
- Routing updates are broadcast
- RIPv2
- A classless distance vector routing protocol that is an enhancement of RIPv1’s features.
- Next hop address is included in updates
- Routing updates are multicast
- The use of authentication is an option
- Similarities between RIPv1 & RIPv2
- Use of timers to prevent routing loops
- Use of split horizon or split horizon with poison reverse
- Use of triggered updates
- Maximum hop count of 15
- Lab Topology
- Scenario:
- 3 router set up
- Topology is discontiguous
- There exists a static summary route
- Static route information can be injected into routing table updates using redistribution.
- Routers 1 & 3 contain VLSM networks
- Scenario Continued
- VLSM
- Recall this is sub netting the subnet
- Private IP addresses are on LAN links
- Public IP addresses are used on WAN links
- Loopback interfaces
- These are virtual interfaces that can be pinged and added to routing table
- Null Interfaces
- This is a virtual interface that does not need to be created or configured
- Traffic sent to a null interface is discarded
- Null interfaces do not send or receive traffic
- Static routes and null interfaces
- null interfaces will serve as the exit interface for static route
- Example of configuring a static supernet route with a null interface
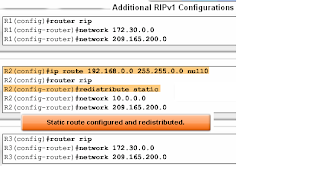
- R2(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
- Route redistribution
- Redistribution command is way to disseminate a static route from one router to another via a routing protocol
- Example R2(config-router)#redistribute static
- Verifying and Testing Connectivity Use the following commands:
- show ip interfaces brief
- ping
- traceroute
- RIPv1 – a classful routing protocol
- Subnet mask are not sent in updates
- Summarizes networks at major network boundaries
- if network is discontiguous and RIPv1 configured convergence will not be reached
- Examining the routing tables
- To examine the contents of routing updates use the debug ip rip command
- If RIPv1 is configured then Subnet masks will not be included with the network address
- RIPv1 does not support VLSM Reason: RIPv1 does not send subnet mask in routing updates
- RIPv1 does summarize routes to the Classful boundary Or uses the Subnet mask of the outgoing interface to determine which subnets to advertise
- No CIDR Support
- In the diagram R2 will not include the static route in its update Reason: Classful routing protocols do not support CIDR routes that are summarized with a smaller mask than the classful subnet mask








Great job and very nice content... i am very glad to read this blog... thanks for sharing this post...
ReplyDeleteVisit my site:- Linksys Router Support